Tokamaks
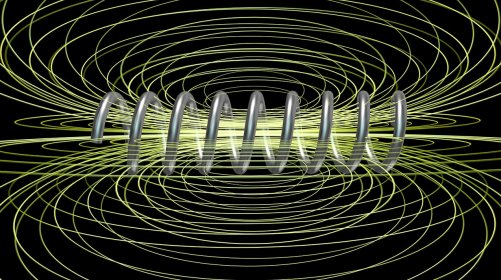
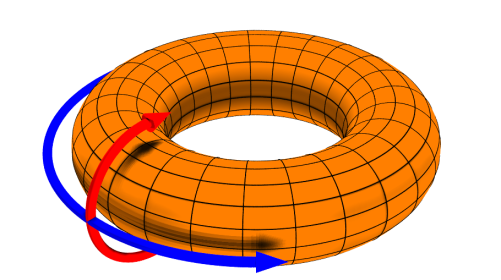
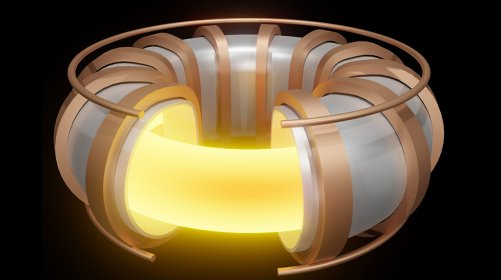
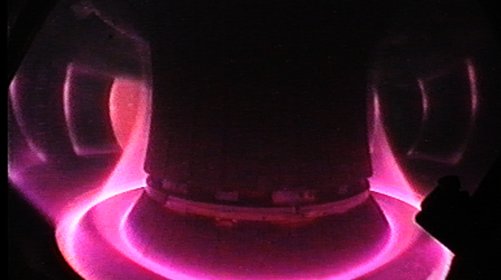
The word "tokamak" is of Russian origin and means "toroidal chamber and magnetic coils." This magnetic confinement system holds plasma in magnetic fields of toroidal shape. The first tokamak, the T-1, started operation in 1958 in Russia, and since then the greatest advances in thermonuclear fusion research have been achieved with tokamaks. The largest tokamak of its time, JET, with a plasma volume of 80 m3, came closest to the scientific breakeven point in 1997, when it achieved Q = 0.67. There are over fifty tokamaks around the world, to name the most important ones: JET, JT-60SA, EAST, WEST, or TFTR. The biggest tokamak in the world, ITER, is now being built in Cadarache, France.