Half-life
4 min read
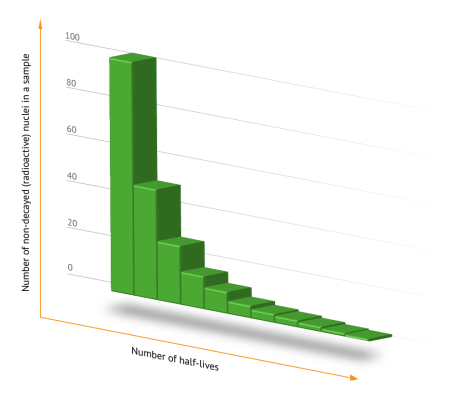
It is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay. However, Ernest Rutherford had already noticed that within a certain period of time, approximately one-half of the atoms decay regardless of how many original atoms there were. He called this period of time the “half-life”. Radioactive decay is a chance event, i.e., there is a definite probability that a nucleus will disintegrate within a certain period of time. Half of the radioactive material disintegrates within the half-life. Half of the remaining radioactive material disintegrates within the next half-life, i.e., one quarter of the original material. After ten half-lives, 99.9 percent of the original material has disintegrated. Each isotope has its specific half-life. Such half-lives range from a few nanoseconds to millions of years.
According to some theories, all atoms are in fact unstable but their half-life can be so long that it cannot be measured.
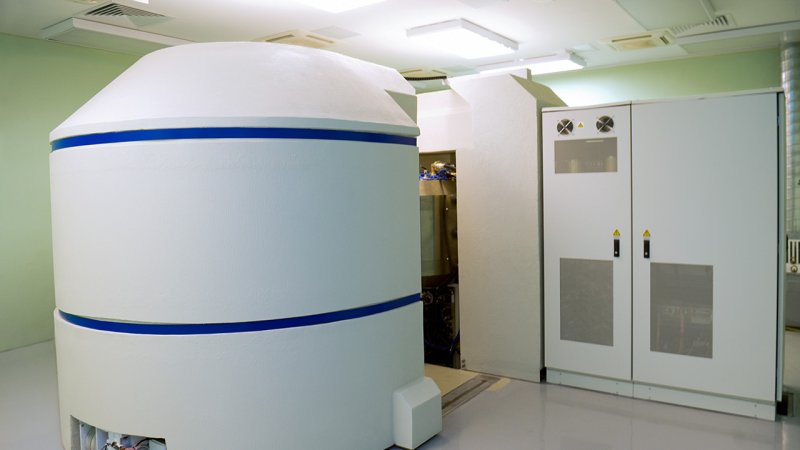
Prior to examination by computer tomography, the doctor administers a contrast medium solution to the patient.
Short-lived Isotopes
Isotopes with a short half-life (primarily iodine 131I and technetium 99mTc) are used in medicine. They are used for contrast imaging, for identification of an organ’s functionality, or as a marker. They disintegrate in the patient’s body very quickly.
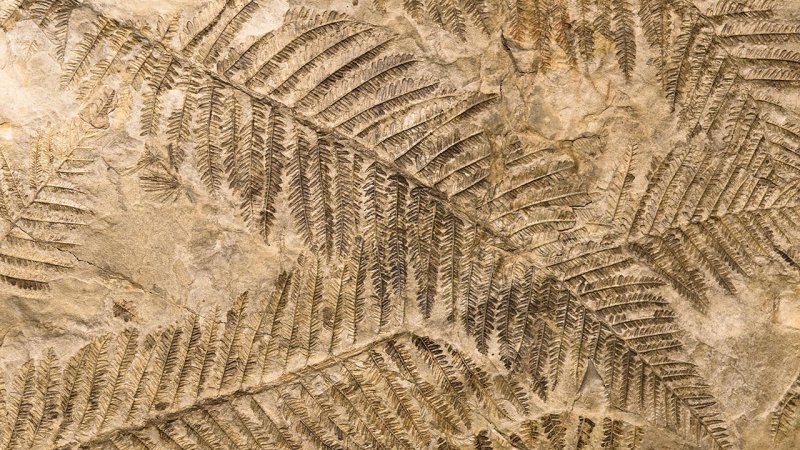
Carbon dating was used to determine the authenticity of the famous Shroud of Turin. Based on the content of the carbon 14C isotope, its age was determined to be about 750 years.
Radiocarbon Dating
The carbon dating method is based on the half-life of the carbon isotope 14C. All living organisms absorb carbon from the environment and use it as a building material. Some of this carbon is in the form of the radioisotope 14C. Every organism contains the same ratio between this isotope and the other carbon isotopes. When an organism dies, the carbon radioisotope starts to decay and this ratio decreases. Following the first half-life, i.e., after 5,730 years, only one-half of the original 14C remains in the sample. By measuring the overall carbon and the radioactive isotope contents, we can determine when the organism died, how many years passed since a plant perished, or when a particular tree was cut down and used to build a ship.
The half-life of iodine 131I is 8 days, of uranium 238U 4.5 billion years, of thorium 223Th 0.9 seconds, of thorium 232Th 14.05 billion years, and of carbon 14C 5,730 years.
Dating of Rocks
In geology, rocks are dated by methods referred to as geochronology. Rocks are dated based on how much of the final isotopes of certain decay series they contain.
The radiocarbon method can be used only for biological samples younger than 60,000 years. Uranium decay can be used for dating rocks. Uranium decays and radiates alpha particles which are then often captured in the surrounding rocks, and by capturing electrons, they become helium atoms. We can evaluate the amount of helium in a sample, evaluate the amount of lead (the final element of the uranium decay series), and then determine the age of the given rock.
In 1988, radiocarbon dating was used to evaluate the authenticity of the Turin Shroud. It was determined that the shroud was made between 1260 and 1390.