Want to ask something?
Send us an e-mail with the subject “Physics mysteries” to the address:
We can't wait to tackle your interesting questions!
How should we understand the decentralization of electricity production?
Previously, electricity generation was centralized because building a power plant was expensive in terms of finance, technology, and materials. Therefore, power plants were initially built either in locations where the relevant source for converting energy into electricity was available (mills and subsequently hydroelectric power plants, coal-fired power plants), and later large-capacity power pla ...
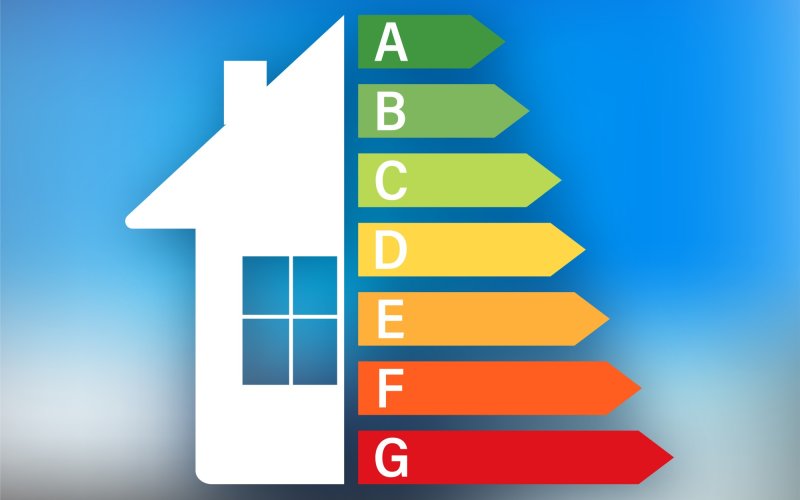
What is a smart grid and how does it work?
With the rapid development of renewable energy sources and their connection to the transmission system, new requirements for its operation have emerged. For us as consumers, they’re not really new — we expect to have electricity available constantly, at the same “quality”, and just as reliably ...
Atom
Imagine taking an apple and cutting it in half. Cut that half in half again, and then cut the resulting piece in half again, and so on ...
Its name means “indivisible”. This concept was introduced some 400 years before our era by the Greek scholar Democritus, who was considering whether matter could be divided indefinitely or not. He came to the conclusion that there must be some small, indivisible particles of matter, and he called them atoms ...
What is the efficiency of different “power plants” (nuclear, coal, solar, wind, hydro, biomass, etc.)?
In every power plant, we convert a selected form of energy into electrical energy. In principle, we use 3 main forms of energy — kinetic energy, light energy, and thermal energy.
We most often use thermal energy, both in coal-fired and nuclear power plants, in biomass-burning power plants, and in some types of solar power plants (those where we use radiation from the sun to heat water or an ...
What are the most effective ways to save energy at home?
Because the largest portion of household consumption is related to heating, the most effective way is to focus on all appliances that produce heat (or remove it — air conditioning).
If we want to consume as little heat as possible, the most effective approach is to start with the most significant measures, namely insulating the house and windows ...
What are the chances of us discovering a previously undiscovered element?
Rather than discovering a new element, it’s more likely that we will create a new element. We have not observed all elements with an atomic number higher than 94 (i.e., with more protons in the nucleus than plutonium has) in nature and therefore have not discovered them, but rather, we have produced them ...
What are the costs of building, operating, and decommissioning a nuclear power plant versus the profit from selling the electricity and heat produced?
Using the example of the planned construction of new units at the Dukovany Nuclear Power Plant, it can be estimated that the investment made will return at least fourfold over the lifespan of the nuclear power plant, even after deducting operating costs, which are relatively low per kWh produced (one-fifth of the kWh price) ...
Is it feasible to store spent nuclear fuel on an uninhabited planet, moon, or in space in the near future?
Technically, it already was and is feasible but the problem lies in the economic aspect. Simply put, radioactive waste can be disposed of quite safely by launching it into Earth’s orbit and then “shooting” it out of the Earth’s gravitational field. This requires a rocket and a simple device to launch a capsule containing radioactive fuel ...
What are the future energy consumption estimates?
Because these are estimates, several different scenarios can be found and they are quite different. In principle, I believe we can expect energy consumption to increase, particularly due to the rise in energy consumption in developing countries (Africa, Asia), where industry will be developing ...
What is the current progress in energy storage technologies?
The development and expansion of energy storage systems are closely tied to the transition toward renewable energy sources. Renewables supply energy only under suitable environmental conditions (when the sun shines or the wind blows) yet these are not always the times when energy is actually needed ...
What is the current ratio of fossil fuel consumption — coal, oil, natural gas — compared to renewable energy sources (such as solar, hydro, etc.)?
Let me first clarify that by fuel consumption, I mean the total energy use across all sectors, not just electricity generation. This distinction is important especially for oil, which is used primarily in transportation rather than in power generation ...
When will we run out of coal and other fossil fuels at the current rate of consumption?
It’s impossible to give a precise answer for several reasons. Global energy consumption is still growing, new fossil fuel deposits may be discovered, extraction efficiency from existing reserves can improve, and previously unused resources — such as shale gas — may become economically viable.
However, if we disregard these factors, the estimates are not particularly optimistic ...
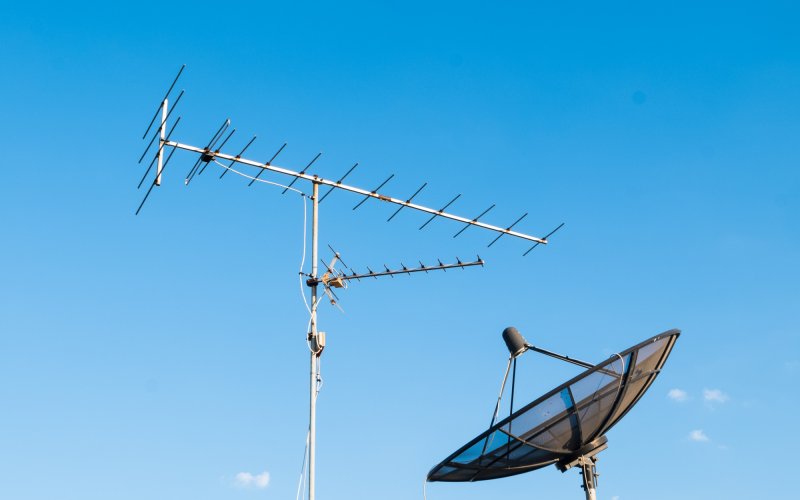
Why are satellite antennas pointed south?
If you want to easily find south (and therefore the other cardinal directions) in an urban area, just look at where the satellite dishes are pointing—in the northern hemisphere, they always poin ...
Why is this the case? Satellite reception is provided (unsurprisingly) by satellites — transmitters that orbit the Earth. One satellite that we are all familiar with is the Moon. It also orbits the Earth. Its period (the time it takes to orbit the Earth) is 27 days, which means that in 27 days it will be in the same place above the Earth ...
Could the Earth be a black hole?
If we wanted to find out how the Earth would have to change to become a “black planet”, all we need is Newton’s law of gravity and Newton’s second law ...
Gravitational force depends on the mass of Earth (6 × 1024 kg) and its radius (6,378 km), while centrifugal force depends on the radius of rotation (i.e., the radius of Earth) and the square of the speed—in the case of a “black planet”, the speed we are dealing with is equal to the speed of light ...
Pressure Cooker — Why Does It Cook Faster?
Physics in the kitchen
Everyone knows that water boils at 100 °C. That’s true – but only at the air pressure we have “at sea level.” If the pressure is increased, water doesn’t start boiling at 100 °C but at a higher temperature ...
Why is a black hole black?
To understand what a black hole is, we first need to think about gravity. Gravity describes the force between two bodies, the magnitude of which depends on the mass of both bodies and the distance bet ...
We can determine the value of the force of gravity from Newton’s law of gravity, from which we can also determine the value of the gravitational field intensity around each body. We all know from experience that if we throw something, it falls back to Earth, and the faster we throw it, the longer it takes for the thrown object to fall back to Earth ...
Why shouldn’t you put hot food in the refrigerator?
There are several reasons why it is recommended to not put hot food in the refrigerator. The first thing that comes to mind is that it increases electricity consumption because the refrigerator has to ...
Because food contains water, it evaporates. The rate of evaporation depends on the temperature, so if the temperature in the refrigerator increases, more water will evaporate from all the stored food. Water will also evaporate from the warm food we put in the refrigerator ...
How did the first polar explorers know they were at the North Pole?
After all, they didn’t have smartphones with GPS back then, and they couldn’t ask anyone for directions, so how did they know they had actually reached the North Pole when there was only s ...
The Earth has two north poles. The first is magnetic and the compass needle points to it. If you let it guide you, it will lead you to the spot where the compass goes “crazy” and starts pointing in all directions. Here, the field lines of the Earth’s magnetic field dive underground, which confuses the compass when it’s horizontal. The position of the magnetic pole changes ...
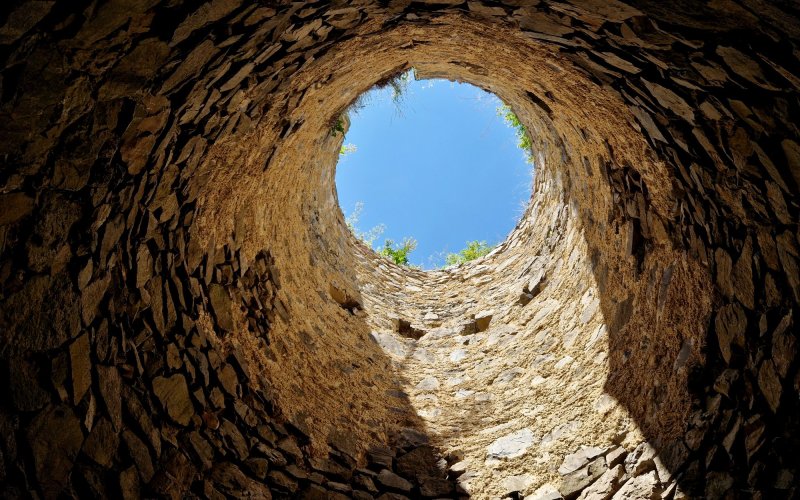
Can I see the stars when I look from the bottom of a deep well?
It was probably Aristotle who first stated that from the bottom of a deep enough well, even on a sunny day, the stars could be seen. This statement was later repeated many times. His assumption was that at the bottom of the well, the shadow would be so deep and dark that the sun would cease to obstruct observation and the stars could be seen ...
How has the development of teleportation progressed?
Are scientists even researching teleportation and how far along are they? When will we finally be able to say “beam me up” and transport ourselves to the other side of the globe?
Surely you’ve thought many times, while stuck in traffic, squeezed in a crowded bus, or wracked by turbulence on a plane, how great it would be to be able to get from place to place without the hassle of travel. If you could walk through a magic door and find yourself in the Seychelles or Paris. If there was a teleport that could take you anywhere you wanted in the blink of an eye ...