- Learning
- Nuclear Fusion Courses
- How Does Thermonuclear Fusion Work?
- Construction and Working Principle of Tokamaks
- Construction and Working Principle of Stellarator
- Inertial Confinement Fusion
- ITER — a Major Step Towards Thermonuclear Fusion
- Fusion Power Plant as a Clean Energy Source
- Basic principles
- Magnetic confinement
- Inertial and electrostatic confinement
- Summative, cross-sectional test — Light version
- Nuclear Energy Courses
- Radioisotopes as Sources of Ionizing Radiation
- Interaction of Atomic Nuclei with Particles
- Nuclear Fuel and the Nuclear Fuel Cycle
- The Principles of Operating a Nuclear Power Plant
- The First Reactor and the First Nuclear Power Plant
- The Most Used Nuclear Reactors: PWR and BWR
- Sources, Processing, and Storage of Radioactive Waste
- Nuclear Power Plant Safety
- Nuclear fuel
- Nuclear fuel and nuclear reactors
- Nuclear power industry
- Nuclear reactors
- Radioactive waste
- Radioactive waste and safety of nuclear power plants
- Nuclear power
- Summative, cross-sectional test — Light version
- Summative, cross-sectional test — PRO version
- Renewable Energy Courses
- Nuclear Fusion Courses
- NUCLEAR fusion
- Energy Space Quest
- NUCLEAR energy
- Nuclear Power Plant Interactive 3D Model
- Nuclear Power
- The Nuclear Power Industry
- Nuclear Fuel
- The Nuclear Reactors
- Reactor Using Fast Neutrons (FR)
- The Future of Fission Reactors
- The Nuclear Power Plant — How it Works
- The First Reactor
- Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)
- Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)
- Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR)
- Gas-cooled Reactor (GCR) and Advanced Gas-cooled Reactor (AGR)
- RBMK Type Reactor
- High Temperature Reactor (HTGR)
- Small Modular Reactors
- NPP PWR Interactive 3D Model
- NPP BWR Interactive 3D Model
- NPP Small Modular Reactors Interactive 3D Model
- AGR Reactor Interactive 3D Model
- CANDU Reactor Interactive 3D Model
- HTGR Reactor Interactive 3D Model
- Superphénix Interactive 3D Model
- Radioactive Waste
- The Safety of Nuclear Power Plants
- Renewable Energy
- WATER energy
- Hydroelectric Power Plant Interactive 3D Model
- Hydroelectric Power Plant Operating Principles
- The Physical Properties of Water
- The Origin of the Water Energy
- History of Water Energy Utilization
- Water Energy and Its Uses
- The Segner Wheel
- Dams and Reservoirs
- Types of Hydroelectric Power Plants
- Kaplan Turbine
- Francis Turbine
- Pelton Turbine
- Choosing a turbine (Turbine selection graph)
- The Highest Dams, the Highest Largest Reservoirs
- The Largest Hydroelectric Power Plants in the World
- Tidal Energy and Sea Wave Power
- Marine Current Power and Ocean Thermal Energy
- HPP Impact on the Environment
- WIND energy
- SOLAR energy
- Solar Power Plant Interactive 3D Model
- Solar Rays Energy
- Ways to Use Solar Heat
- Solar Collectors
- Solar Concentrators
- Central Tower Solar Power Plants
- Solar Farms
- The Largest Solar Power Plants
- The Energy Use of the Photovoltaic Effect
- Photovoltaic Farms
- Solar Energy and the Environment
- Solar Energy and Solar Power Systems Summary
- GEOTHERMAL energy
- BIOMASS energy
- The FUTURE of Renewable Energy Sources
- WATER energy
- 3D models
- Free Downloads
- Physics mysteries
- Scientific breakeven
- Scram
- Scrape-off layer, SOL
- Secondary circuit
- Segner wheel
- Semiconductor
- Shaft
- Shut-off (emergency) rod
- Sievert, Sv
- Single-null-divertor
- Small hydroelectric power plant
- Sodium, Na
- Solar (thermal) collector
- Solar concentrator
- Solar farm
- Solar hot air collector
- Solar radiation
- Solar thermal power plant
- Solar updraft tower
- Speed of the wind
- Spent (burnt) fuel
- Spherical tokamak
- Spheromak
- Spillway
- Star
- Steam cycle
- Steam generator
- Stellarator
- Stirling engine
- Strobe effect
- Strontium, Sr
- Subcritical state
- Sun
- Superconductor
- Supercritical state
- Superheated water
- Supernova
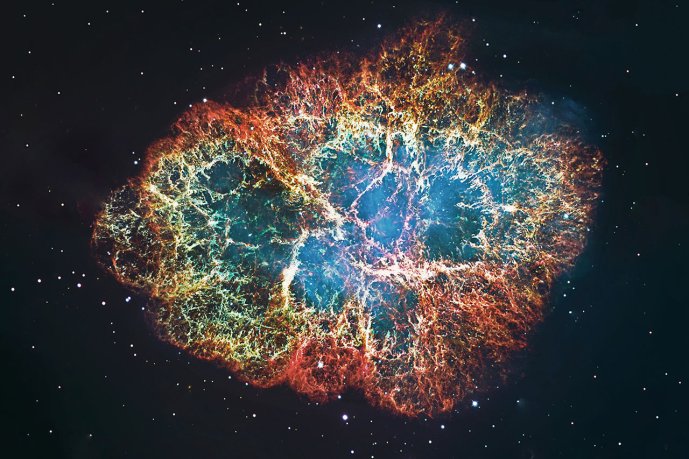
Supernova
A cataclysmic event that terminates the life of a star with a mass of about 12 Suns or more with a huge explosion in which most of the star is blown apart. When the star has exhausted the light elements for fusion, heavy elements (e.g. iron) begin to accumulate in its core, from which the star gains no more energy by fusion. Thus, it cannot resist gravitational pressure and the core collapses into a massive neutron star or even a black hole. The shock wave that this collapse causes in the outer layers of the stellar material will violently blast them away into the surroundings. The exact reasons of stellar core collapse vary according to the properties of the star, its size and its chemical composition. A supernova shines so intensely over almost the entire electromagnetic spectrum that a supernova hundreds of thousands of light years away can be seen with the naked eye in the Earth’s sky.
ABOUT US
Energy Encyclopedia (EE) is the project of Simopt. We have devoted ourselves to popularizing energetics in an educational and entertaining way since 1991. In the following years, we plan to continue the development of EE.
If you have a serious interest in creating a localized version, please contact us.